Antefix with female head
Summary
The polychromy on the antefix is rather well-preserved. The colour palette is comprises calcite, yellow ochre, red ochre, umber, carbon black and Egyptian blue. Nuances are achieved by superposition of layers of different hues rather than mixing of pigments. Mineral clays constitute an essential part of the entire stratigraphy suggesting that diluted clay has been used as a binder for the pigments.
Description of object
Antefix with female head antefix is made of pale to very pale brown clay (10YR 6/3-7/3). It is restored from many fragments and is missing parts of the shell frame. The antefix is decorated with a female head surrounded by a deeply curved floral shell. The female wears a diadem and very large earrings of the type termed “a grappolo”. Her wavy hair is parted in the middle and drawn to the sides. Around her neck is a piece of drapery. Her face is oval with widely spaced eyes and a long thin nose. The shell has three large palmettes, each consisting of seven leaves alternating with lotus flowers.
Archaeological Commentary
At least seven further examples of this type of antefix are known, all also said to be from Cerveteri: one in the Vatican (Museo Gregoriano Etrusco, inv. no. 13978), one in Berlin (Antikensammlung, inv. no. 6681), three in Philadelphia (Penn University Museum, inv. nos. MS 1802, 1803, 1826. Turfa 2005, no. 289, 290, 291), two in London (British Museum, inv. nos. 1893,0628.2; 1893,0628.3), and one in New York (Metropolitan Museum of Art, inv. no. 96.18.158).
Choice of methods
Visual examination
- Macroscopic
- Microscopic in situ
Technical imaging
- UV
- VIL
Sampling
- Cross section
- Microscopy
- SEM/EDX
- XRF
Visual examination
The female head has bright white skin. The eyelids, cheekbones, alas, nostrils, mentolabial groove, and necklace lines are accentuated in a pale, peachy color. The lips are painted red with broad, fluent, yet less attentive brush strokes. The eyes are brown with black pupils, rims, and brows. The hair is painted a reddish brown with yellowish highlights. The earrings and diadem are painted a bright yellow. The latter has gemstones in red. The textile draping the female’s neck is also red merging with the inner part of the shell frame. The palmette petals and the lotus flowers are painted in white, light blue, and a yellowish brown contrasting with a murky, bluish background color. The latter has been rather carelessly applied. The base is decorated with a geometric pattern in black, white, and red separated from the base by a brownish line.
Technical imaging
UV-FL: Due to the fluorescence of the glue, the joints light up in the UV. Some joints fluoresce red others light blue indicating different types of glue. Two areas on the face fluoresce. The reason for this has, however, not been determined.
VIL: The VIL-imaging reveals the extensive use of Egyptian blue on the shell frame on the background around the palmettes and the outer leaves of the lotus flower which means that black is mixed with Egyptian blue to obtain a bluish-black effect. An even distribution of relatively large grains is observed on the white skin and the white areas on the base. Furthermore, the yellow jewelry displays a very even distribution of minute grains of Egyptian blue.
Other types of investigation
XRF in situ:01: Terracotta: Ca, Fe, K and S. 02: White on palmette: No distinct differences from terracotta reading. 03: White skin: Relatively high level of Ca indicating calcite or similar Ca-based white. 04: Peachy accentuation: Large amount of Ca and raised levels of S and P, Ca-based colour. 05: Yellow earring: Ca, Fe and S indicating yellow ochre mixed with calcite or other Ca-based white pigment. 06: Yellowish brown hair: Large amount of Fe, probably ochre pigments. 07: Red drapery: Large amount of Fe, probably red ochre. 08: Blue on lotus flower: Significant content of Cu indicates copper-based blue.
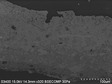
A sampling strategy was developed on the basis of the preliminary investigation. Four samples with a surface area of c. 1 mm2 were collected. Sample 1: Lower necklace line. Sample 2: Highlight in the hair. Sample 3 and 4: Background colour of a palmette. The samples were prepared as cross-sections and examined with an optical microscope.
SEM-EDS (point analysis): Only sample 1 was examined using SEM-EDS. The white skin colour is based on calcium carbonate (CaCO3) which is mixed with compounds rich on silicon and aluminum – possibly kaolinite (Al2Si2O5(OH)4). Thus, the pigment is based on calcite and contains other compounds indicating kaolin. The peachy accentuation consists of iron compounds suggesting hematite (α-Fe2O3), i.e. red ochre. In addition, mineral clays constitute an essential part of the stratigraphy. The chemical composition of these clay minerals indicates the use of kaolin (Al2Si2O5(OH)4). Usually, kaolin is easily recognizable with SEM due to its highly characteristic, hexagonal, plate-like shape. However, when exposed to firing temperatures excessing 500 °C, it loses its crystallographic order as it forms metakaolin.
Bibliography
C. Brøns, S.B. Hedegaard & M.L. Sargent Forthcoming, Painted Faces: Investigations into the polychromy of Etruscan antefixes, in Etruscan Studies.
J. Christiansen & N.A. Winter (2010), Etruria I. Catalogue. Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek, Copenhagen, 108, cat. no. 49.
C. Brøns, S.B. Hedegaard & K.L. Rasmussen (2018), The real thing? Studies of polychromy and Authenticity of Etruscan Pinakes at the Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek. Studi Etruschi LXXIX – MMXIV, 195-223.
S.B. Hedegaard (2018), Reconstructing Etruscan Architectural Polychromy: Antefixes from the Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek, in S. Bracci, G. Giachi, P. Liverani, P. Pallecchi & F. Paolucci (eds.) Polychromy in Ancient Sculpture and Architecture. Proceedings of the 7th Round Table, Florence, 4-7 November 2015, Sillabe, Florence, 36-42.
- HIN 70
- Antefix
- Late 4th cent. B.C.E.
- Classical
- Terracotta
- Acquired by the Ny Carlsberg Glyptotek in 1892.
- H. 47 cm.; W. 48 cm.